This article provides a detailed legal guide of establishing and operating a foreign-invested business, including the fdi process in Nepal, its approval, obtaining fdi advisory services along with statutory requirements.
Foreign investors seeking to establish a business in Nepal are generally required to commit a minimum investment of USD 150,000 in permitted sectors. However, this minimum investment requirement does not apply to Information Technology (IT) companies.
In order for foreign nationals to establish a business in Nepal, it is mandatory to register either a private or public limited company under the fdi process in nepal. Such registration must be completed with the Department of Industry, the Office of the Company Registrar, and the Nepal Rastra Bank.
How can Foreigners & Foreign Companies establish entity in Nepal?
Foreigners and foreign companies can establish business entities in Nepal through several pathways defined under the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA) 2019. The process begins with obtaining investment approval from the Department of Industry (DOI) through the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer (FITT) Unit of the One Stop Service Center (OSSC).
The establishment process varies based on the investment amount, business sector, and ownership structure. Foreign investors must comply with minimum investment thresholds (generally NPR 20 million, with exceptions for IT companies) and sector-specific foreign equity caps as prescribed by law.
What constitutes Foreign Direct Investment under Nepali Law?
Under Section 2(h) of the Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA) 2019, Foreign Direct Investment in Nepal encompasses several distinct forms of capital contribution and business engagement by foreign entities or individuals. The law recognizes the following as legitimate modes of FDI:
- Foreign currency investment in equity shares of Nepalese companies
- Investment through leasing of foreign-owned machinery, equipment, and technology
- Investment via internationally recognized venture capital funds
- Technology transfer through licensing, franchising, or technical assistance agreements
- Reinvestment of profits earned from existing foreign investments in Nepal
- Investment through issuance of securities in foreign stock markets
- Investment in Nepal’s secondary stock market through designated instruments
What legal structures are available for establishing a business in Nepal?
The Companies Act 2063 (2006) provides multiple legal structures for establishing businesses in Nepal with foreign investment. Foreign investors can choose from the following business entities:
| Type of Entity | Shareholder Requirement | Legal Status | Key Features | Naming |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private Limited Company | Minimum: 1Maximum: 101 | Separate legal entity with limited liability | Most common for foreign investors; offers management flexibility and liability protection. | Must end with “Private Limited” or “Pvt. Ltd.” |
| Public Limited Company | Minimum: 7Maximum: No limit | Separate legal entity; subject to heightened regulatory scrutiny | Permitted to raise capital from the public; regulated by the Securities Board of Nepal. | Must end with “Limited” or “Ltd.” |
| Branch Office | Not applicable (extension of parent company) | Not a separate legal entity | Operates only within approved activities; directly accountable to the foreign parent entity. | Uses parent company name with “Branch Office” |
| Liaison/Representative Office | Not applicable | Not a separate legal entity | Used for non-commercial activities such as market research and coordination; no revenue-generating operations allowed. | Uses parent company name with “Representative Office” |
| Joint Venture | As agreed by parties involved | May be incorporated or contractual | Formed with Nepali partners; may be structured as a registered company or a contractual agreement for specific projects. | Depends on structure and agreement |
Each structure has distinct registration requirements, liability implications, and operational limitations under Nepali law. The selection depends on business objectives, investment scale, and sector-specific regulations which can be achieved through our FDI Related Advisory Service in Nepal.
Which sectors are open to foreign investment in Nepal?
Nepal’s Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA) 2019 and the Industrial Enterprises Act 2020 adopt a negative list approach, meaning all sectors are open to foreign investment except those specifically restricted. According to Section 3 of FITTA 2019, the following sectors are open for foreign investment:
- Hydropower and renewable energy
- Manufacturing industries
- Tourism (hotels, resorts, adventure tourism)
- Information technology and business process outsourcing
- Infrastructure development (roads, airports, tunnels)
- Agriculture and agro-processing
- Mining and mineral-based industries
- Health services and education
- Financial services (with specific regulations)
Restricted sectors under Section 4 of FITTA 2019 include:
- Primary agriculture (excluding commercial farming)
- Poultry farming and fisheries (below specified thresholds)
- Personal service businesses (beauty parlors, tailoring)
- Arms and ammunition manufacturing
- Real estate business (excluding construction)
- Retail business (with exceptions for branded chains)
- Local courier services and atomic energy
Additionally, certain sectors have foreign equity caps, such as telecommunications (80%), domestic airlines (49%), and consultancy services (51%). The Investment Board Nepal handles large-scale investments exceeding NPR 6 billion, while the Department of Industry conducts the fdi process in nepal.
What are the legal requirements for Incorporating FDI Company?
Incorporating a business with foreign investment in Nepal requires fulfilling several legal prerequisites under the Companies Act 2063 (2006) and FITTA 2019. The essential requirements include:
- Prior approval from the Department of Industry through the FITT Unit of OSSC is mandatory before company registration.
- Foreign investors must meet the minimum investment threshold of NPR 20 million (approximately USD 150,000), except for IT companies which have no minimum threshold.
- A physical address in Nepal must be designated as the registered office of the company.
- At least one director is required for private limited companies, while public limited companies need a minimum of three directors.
- The Capital must be injected into a Local Bank through approval of Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB).
The incorporation process must follow the sequence established by law, with FDI approval necessarily preceding company registration.
FDI Related Advisory and Approval Service in Nepal
In the private sector, specialized law firms and consultancies like Tax Consultant Nepal (TCN) and Axion Partners offer professional advisory services covering legal compliance, tax planning, and strategic guidance for foreign investors. The firm assist with document preparation, representation before regulatory authorities, and ongoing compliance management along with 1-Month FDI Approval Service in Nepal.
What are the sectoral thresholds or caps on foreign investment?
Nepal imposes specific sectoral caps on foreign investment to balance international capital inflow with domestic industry protection. These limitations are established under FITTA 2019 and sector-specific regulations:
| Sector | Maximum Foreign Ownership | Regulatory Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Consultancy Services | 51% | Department of Industry / Relevant Professional Bodies |
| Telecommunications | 80% | Nepal Telecommunications Authority (NTA) |
| International Air Operators | 80% | Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal (CAAN) |
| Domestic Air Operators | 49% | Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal (CAAN) |
| Approved Training Organizations (ATO) | 95% | Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal (CAAN) |
What is the procedure for Foreign Direct Investment in Nepal?
Foreign Direct Investment Procedure
- Step 1: Online Application through imis.doind.gov.np
- Step 2: FDI Approval from FITT Unit of OSSC
- Step 3: Incorporation of Company from OCR unit of OSSC
- Step 4: Approval for FDI Inflow from NRB Unit at OSSC
- Step 5: Registration of PAN/VAT from IRO Unit of OSSC
- Step 6: Industry Registration at DOI
- Step 7: Opening of Bank Account and Remitting the Investment
- Step 8: Recording of the Investment Nepal Rastra Bank
- Step 9: Approval of Environmental Study from Competent Authority
- Step 10: Construction/Establishment of Industry from the Investor
- Step 11: Information of Operation of Industry
Step 1: Online Application through imis.doind.gov.np
The first step in the investment process is submitting an online application via the imis.doing.gov.np portal, where applicants provide necessary details for foreign investment registration and processing approval.
Step 2: FDI Approval from FITT Unit of OSSC
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) approval is sought from the FITT unit at the OSSC. This step ensures that the investment complies with local regulations and is in line with economic policies.
Step 3: Incorporation of Company from OCR unit of OSSC
After FDI approval, the company is incorporated through the OCR unit at OSSC. This step involves registering the business entity to legally establish operations within Nepal under applicable laws.
Step 4: Approval for FDI Inflow from NRB Unit at OSSC
Approval for the inflow of foreign direct investment is obtained from the NRB unit at OSSC. This ensures compliance with financial regulations, including foreign exchange controls and remittance procedures.
Step 5: Registration of PAN/VAT from IRO Unit of OSSC
Businesses are required to register for PAN and VAT at the IRO unit of OSSC. These registrations are necessary for tax compliance and to carry out business transactions legally within Nepal.
Step 6: Industry Registration at DOI
Registering the industry at the Department of Industry (DOI) is a crucial step for legal recognition. This process ensures the business meets sector-specific requirements for operation and enjoys legal protections. These procedures can be completed through our expert FDI Advisory Services in Nepal.
Step 7: Opening of Bank Account and Remitting the Investment
Investors must open a bank account in Nepal and remit their investment capital as part of the legal requirements. This step ensures that the investment is deposited into a recognized financial institution.
Step 8: Recording of the Investment at Nepal Rastra Bank
The investment must be officially recorded with Nepal Rastra Bank to comply with regulations governing foreign investments. This step ensures transparency and proper documentation of the foreign capital inflow.
Step 9: Approval of Environmental Study from Competent Authority
An environmental study is required for industry projects, and approval from the competent authority ensures the business adheres to environmental laws and practices, safeguarding Nepal’s environmental health and sustainability.
Step 10: Construction/Establishment of Industry from the Investor
Following regulatory approvals, the investor may proceed with the construction or establishment of the industrial facility. This stage involves building the infrastructure required to begin operations in the industry.
Step 11: Information of Operation of Industry
Once the industry is operational, the relevant authorities must be informed of the commencement of business activities. This ensures that the business complies with ongoing reporting and operational regulations.
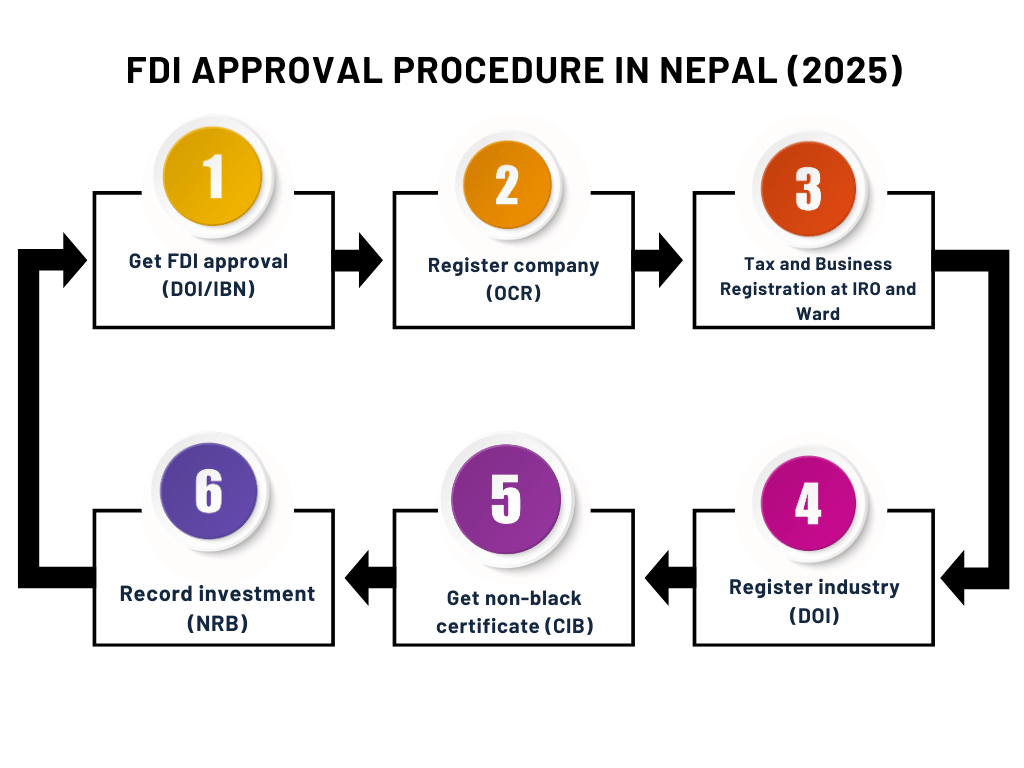
How to Get FDI Approval in Nepal?
FDI Approval in Nepal
- Step 1: Obtain FDI Approval from the Department of Industry
- Step 2: Registration of Company at OCR
- Step 3: Tax and Business Registration at IRO & Ward
- Step 4: Recommendation and Registration of Industry at DOI
- Step 5: Opening Bank Account and Recording Investment at NRB
What are the documents required for FDI Approval in Nepal?
The Department of Industry requires a specific set of documents for processing FDI process in Nepal. These documents must be submitted through the online portal (imis.doind.gov.np):
Documents Required for FDI Approval in Nepal
- Online Application Form completed through the DOI Portal
- Project Proposal signed and stamped by all investors, detailing business objectives, market analysis, implementation timeline, employment generation, and financial projections
- Joint Venture Agreement (for multiple investors) with clear terms on capital contribution, profit sharing, management rights, and dispute resolution mechanisms
- Notarized Copies of Citizenship Certificate of Local Partner(s) or Certificate of Incorporation if the local party is a company
- Notarized Copy of Passport of Foreign Investor(s) or Certificate of Incorporation including Memorandum and Articles of Association if the foreign party is a company
- Bio Data of Foreign Individual Investor or Company Profile signed by authorized representative
- Financial Credibility Certificate issued by a bank in the investor’s home country, confirming financial capacity to make the proposed investment
- Letter of Authorization if application is submitted by a representative
FDI through Share Transfer in Nepal through Share Purchase Agreement
- Online Application through the DOI Portal from the share transferor
- Share Transfer Agreements signed by both parties
- Notarized Board Meeting Minutes approving the share transfer
- Current Shareholders list certified by the Office of Company Registrar
- Latest Audited Financial Statements
- Tax Clearance Certificate or extension certificate
- All identification documents of the foreign investor as required for new projects
All foreign-language documents must be accompanied by notarized English translations. The Department may request additional documents based on the nature and complexity of the proposed investment.
What is the timeline for completing a Foreign Company Incorporation?
The timeline for completing foreign company incorporation in Nepal follows a sequential process with specific durations for each stage. The complete fdi process in Nepal typically takes 30-45 days from initial application to operational readiness:
| Procedure | TCN Timeline |
|---|---|
| FDI Approval | 1-2 Weeks |
| Company Registration | 3-5 Days |
| NRB Approval for Capital Inflow | Takes 2–3 working days following company registration; granted by Nepal Rastra Bank to permit foreign capital inflow. |
| PAN/VAT Registration | Completed within 1–2 working days after company registration; managed by the Inland Revenue Office unit at OSSC. |
| Industry Registration | Takes 5–7 working days after PAN/VAT registration; involves business classification and registration with the Department of Industry. |
| Bank Account Opening | Requires 2–3 working days, depending on the internal due diligence procedures of the selected commercial bank. |
| Capital Remittance and Recording | Transfer takes 3–7 days via international banking channels; NRB recording requires an additional 2–3 days. |
| Environmental Approvals (if applicable) | Requires 45-60 days based on business nature and the level of environmental assessment required by law. |
The timeline can extend if the project requires additional sector-specific approvals or if documentation is incomplete. Investors must also adhere to the investment timeline requirements as for fdi in nepal what are mandated that 5-25% of approved investment (depending on total amount) must be brought into Nepal within one year of approval.
Which sectors are prioritized for foreign investment?
Nepal’s government has designated certain sectors as priority areas for foreign investment, offering enhanced incentives and streamlined processes, as its required for FDI in Nepal. These prioritized sectors align with national development goals and are identified in the Industrial Policy, FITTA 2019, and various sector-specific policies:
| Sector | Details |
|---|---|
| Hydropower and Renewable Energy | Nepal encourages FDI in power generation, transmission, and distribution; guided by the Electricity Act and Hydropower Development Policy. |
| Tourism Infrastructure | Priority status for high-end hotels, resorts, adventure tourism, and convention centers; governed by the Tourism Policy. |
| Transportation Infrastructure | Roads, railways, airports, cable cars, and urban transit prioritized under the Public-Private Partnership and Investment Act, 2019. |
| Information Technology | IT parks, BPO, data centers, and software ventures prioritized with special incentives, including exemption from minimum investment thresholds. |
| Agriculture and Agro-processing | Commercial farming, food processing, cold storage, and agro-tech receive priority under the Agriculture Development Strategy. |
| Manufacturing Industries | Focus on export-oriented, pharmaceutical, and local-resource-based industries with favorable investment provisions. |
| Health and Education | Investment encouraged in specialized hospitals and international-standard educational institutions through targeted incentives. |
What benefits or incentives are available to foreign-invested industries?
Nepal offers a comprehensive package of fiscal and non-fiscal incentives to attract foreign investment across various sectors. These incentives are primarily governed by the Income Tax Act 2058 (2002), Industrial Enterprises Act 2076 (2020), and FITTA 2019:
Tax Incentives in Nepal for Foreign Investors
- 40% tax concession for infrastructure investments including transportation, power generation, and telecommunications
- 20% tax reduction for manufacturing industries with an additional 5% concession on income derived from exports
- Graduated tax concessions of 90%, 80%, and 70% for manufacturing industries established in underdeveloped, undeveloped, and less developed regions respectively
- 50% income tax concession for tea production, dairy, and textile industries
- Full income tax exemption for 5 years for investments exceeding NPR 1 billion that create at least 500 employment opportunities
- Complete income tax exemption for power projects for the first 10 years and 50% exemption for the subsequent 5 years
- Full income tax exemption for 7 years and 50% exemption for the next 3 years for mineral extraction and processing industries
- 100% tax exemption for 10 years and 50% for the next 5 years for tourism investments exceeding NPR 2 billion
- Up to 25% tax reduction based on employment generation for specified industries
Non-Fiscal Incentives in Nepal
- Customs duty exemptions on capital goods and raw materials for export-oriented industries
- Simplified visa procedures for foreign investors and technical experts
- Land acquisition facilitation for priority sector investments
- One-stop service for regulatory approvals
- Protection against nationalization and expropriation
- Guaranteed repatriation rights for dividends and invested capital
These incentives vary by sector, investment size, location, and employment generation capacity, creating a tiered system that rewards larger investments in priority sectors and underdeveloped regions.
Which laws and regulatory bodies govern FDI in Nepal?
Foreign Direct Investment in Nepal is governed by a comprehensive legal framework administered by multiple regulatory bodies. The primary laws and regulations include:
| Legal/Regulatory Instrument or Body | Description |
|---|---|
| Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA) 2019 | Core legislation defining permitted foreign investment types, approval processes, repatriation rights, and restricted sectors. |
| FITTA Regulations 2021 | Detailed procedural framework for FDI process in nepal, technology transfer agreements, and investor compliance obligations. |
| Industrial Enterprises Act 2020 | Defines industrial classifications, registration protocols, and incentive mechanisms for foreign-invested enterprises. |
| Companies Act 2063 (2006) | Governs incorporation, governance, and compliance for all companies, including foreign-invested entities. |
| Nepal Rastra Bank Act 2058 (2002) and Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 2019 | Regulate foreign currency operations, capital inflow, and profit repatriation mechanisms. |
| Securities Act 2063 (2007) | Regulates public offerings and investment through Nepal’s securities markets. |
| Department of Industry | Primary FDI approving body for investments below NPR 6 billion; monitors compliance. |
| Investment Board Nepal | Handles large-scale and strategic investments exceeding NPR 6 billion. |
| Nepal Rastra Bank | Regulates the foreign exchange components of FDI, including approval of capital inflows and repatriation. |
| Office of Company Registrar | Responsible for company incorporation and ensuring compliance with corporate governance standards. |
| Sector-specific Regulatory Authorities | Includes bodies like NTA, Insurance Board, and SEBON; oversee sector-specific foreign investment compliance. |
| One Stop Service Center (OSSC) | Integrated government facility streamlining FDI approvals via representatives from multiple relevant agencies. |
This multi-layered regulatory framework ensures comprehensive oversight while the OSSC mechanism aims to reduce bureaucratic hurdles for investors. FDI Companies are similar to LLC Companies, in terms of their rights, characteristics and liabilities.
What is the process for obtaining sector-specific investment approvals?
Beyond the standard FDI process in Nepal and its approval, foreign investors must obtain sector-specific approvals depending on their business activities. These specialized approvals ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards:
| Sector | Regulatory and Procedural Requirements |
|---|---|
| Banking and Financial Institutions | – Preliminary approval from Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) – Fulfillment of capital requirements per financial category – Fit and proper assessment of promoters/directors – Final licensing after company registration |
| Telecommunications | – Technical and financial evaluation by Nepal Telecommunications Authority (NTA) – Spectrum allocation approval (if applicable) – Service-specific licensing based on telecom type |
| Hydropower Projects | – Survey license from Department of Electricity Development (DoED) – Power Purchase Agreement with Nepal Electricity Authority – Generation license post-environmental compliance – Grid connection agreement |
| Tourism Enterprises | – Hotel classification approval by Department of Tourism – Licensing for trekking and travel agencies – Permits for adventure tourism activities |
| Healthcare Facilities | – Approval from Ministry of Health and Population – Compliance certification with applicable health facility standards – Registration of clinical staff with Medical Council |
| Education Institutions | – Approval from Ministry of Education, Science and Technology – Curriculum approval by designated education boards – University affiliation for higher education institutions |
The sector-specific approval processes run parallel to or following the standard FDI approval. These specialized permits typically require submission of detailed operational plans, technical specifications, and compliance commitments relevant to the specific industry standards and regulations.
What are the official government fees and charges for FDI Company?
Establishing a company through FDI Process in Nepal involves various official government fees and charges payable at different stages of the process which is an estimate and proper legal consulting is recommended:
Below is the requested information formatted into a table with two columns:
| Fee Type | Details |
|---|---|
| FDI Approval Fees | NPR 25,000 Security Deposit |
| Company Registration Fees | Based on the Authorized Capital from NPR 1,000 to NPR 43,000+ |
| Tax Registration Charges | No fee |
| Industry Registration Fees | – |
| Environmental Approval Fees | Depends on the Project |
| Banking Charges | – |
| Annual Renewal Fees | – |
What are the post-investment compliances for such company?
Foreign-invested companies in Nepal must adhere to various post-investment compliance requirements after FDI Approval Process to maintain good standing with regulatory authorities:
| Compliance Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Annual Filings and Renewals | – Annual return submission to Office of Company Registrar within 3 months of fiscal year-end – Audited financial statements filing with tax authorities within 3 months of fiscal year-end – Industry registration renewal annually with the Department of Industry – Tax clearance certificate after annual tax assessment |
| Foreign Investment Reporting | – Quarterly reporting of foreign currency transactions to Nepal Rastra Bank – Annual verification of foreign investment status with Department of Industry – Notification of changes in foreign shareholding pattern – Reporting of technology transfer fee payments and royalty remittances |
| Corporate Governance Compliances | – Conducting Annual General Meeting within 6 months of fiscal year-end – Maintaining statutory registers including share register and minutes books – Updating company details upon changes in directors, address, or capital structure – Compliance with CSR requirements (2% of annual profit for companies with turnover exceeding specified thresholds) |
| Employment and Labor Compliances | – Social Security Fund contributions (31% of basic salary: 20% employer, 11% employee) – Provident Fund and Gratuity provisions as applicable – Work permit renewals for foreign employees – Compliance with local employment quotas (minimum 80% Nepali nationals) |
| Environmental Compliances | – Periodic environmental audits as specified in environmental clearances – Implementation and monitoring of pollution control measures – Compliance with waste management regulations |
Foreign-invested companies must also adhere to sector-specific compliance requirements imposed by industry regulators. Failure to maintain these compliances can result in penalties, restrictions on repatriation rights, or in severe cases, revocation of business licenses.
What tax regime applies to foreign-invested entities?
Foreign-invested entities in Nepal are subject to the same tax regime as domestic companies, with certain specific provisions related to cross-border transactions:
| Tax Type | Details |
|---|---|
| Corporate Income Tax | – Standard rate: 25% on taxable income – Reduced rate: 20% for manufacturing enterprises – Special rates: 30% for banks, financial institutions, tobacco, alcohol, telecommunications, and courier services – Quarterly advance tax payments based on estimated annual income |
| Value Added Tax (VAT) | – Standard rate: 13% on most goods and services – Zero-rated VAT for exports and specified goods/services – Registration mandatory for businesses with turnover exceeding NPR 5 million |
| Withholding Taxes | – Dividend distribution to foreign shareholders: 5% final withholding tax – Interest payments to non-residents: 15% withholding tax – Service fees, royalties, technical service fees to non-residents: 15% withholding tax – Management fees: 15% withholding tax |
| Capital Gains Tax | – 25% on gains from business asset disposal – 10% on gains from sale of shares in unlisted companies – 5% on gains from sale of shares in listed companies |
| Customs and Import Duties | – Rates vary based on goods type, ranging from 0-80% – Exemptions for certain capital goods and raw materials for export-oriented industries |
| Double Taxation Avoidance | – Agreements with 10+ countries (including China, India, South Korea, and Europe) ‘ – Treaty provisions may reduce withholding tax rates on cross-border payments |
Tax incentives described earlier apply equally to foreign-invested entities based on sector, location, and employment generation. Foreign investors should conduct comprehensive tax planning considering both Nepali tax laws and those of their home jurisdiction.
Can I repatriate profits? How can profits be lawfully repatriated by foreign Investors?
Yes, foreign investors can lawfully repatriate profits from Nepal. The Foreign Investment and Technology Transfer Act (FITTA) 2019 explicitly guarantees the right to repatriate dividends, profits, proceeds from share sales, loan repayments, and technology transfer fees. The process for lawful repatriation involves:
Dividend Repatriation:
- Board resolution approving dividend distribution
- Shareholder resolution confirming dividend declaration
- Tax clearance certificate from Inland Revenue Department
- Payment of applicable dividend withholding tax (5%)
- Application to commercial bank with supporting documents
- NRB approval through the bank for amounts exceeding USD 5,000
Capital Repatriation (from share sale or liquidation):
- Documentation of original investment through Form A registration
- Proof of share transfer or company liquidation
- Valuation report for unlisted companies
- Capital gains tax payment evidence
- Application through authorized bank to Nepal Rastra Bank
Technology Transfer Fee Repatriation:
- Approved technology transfer agreement registered with DOI
- Invoice for royalty or fee as per agreement terms
- Withholding tax payment evidence (15%)
- Application through banking channel
Loan Repayment:
- Evidence of loan registration with NRB at the time of inflow
- Loan agreement and repayment schedule
- Tax clearance on interest payments
- Application through the same bank that received the loan
The repatriation process typically takes 7-14 days once all documentation is complete. There are no restrictions on the amount that can be repatriated, provided the funds represent legitimate returns on registered foreign investment and all tax obligations have been fulfilled. Nepal Rastra Bank maintains oversight of all repatriations to ensure compliance with foreign exchange regulations.
How can foreign investors obtain business visas in Nepal?
Foreign investors can obtain business visas in Nepal through a structured process that varies based on investment amount and business purpose. The Department of Immigration handles visa issuance with input from relevant ministries:
For Non-Resident Business Visa:
- Application submission to Department of Immigration
- Recommendation letter from Department of Industry confirming FDI process in nepal
- Proof of minimum USD 100,000 investment or equivalent
- Company registration documents
- Personal identification documents (passport valid for at least 6 months)
- Visa application form and photographs
- Visa fee payment (approximately USD 250 for one year)
For Residential Business Visa:
- Evidence of investment exceeding USD 100,000
- Recommendation from Department of Industry
- Tax clearance certificate
- Company operational status verification
- Proof of physical presence requirement fulfillment
For Business Visa Extension:
- Application at least 15 days before expiration
- Updated company status report
- Tax compliance evidence
- Proof of continued investment
The initial business visa is typically granted for one year and can be extended annually upon verification of continued business operations and investment. Investors with investments exceeding USD 1 million may qualify for multiple-year visas.
Family members of foreign investors can obtain dependent visas based on the investor’s business visa status. The business visa allows multiple entries and exits from Nepal during its validity period.
Foreign technical experts and employees working in FDI companies can obtain non-tourist working visas based on employer recommendations and work permit approvals from the Department of Labor.
FAQs
How to Obtain FDI Related Advisory Service in Nepal?
FDI advisory services in Nepal are provided by the Department of Industry, Investment Board Nepal, and private consultancies like Tax Consultant Nepal (TCN) and Axion Partners who offer specialized guidance on legal compliance and investment procedures.
What is the FDI Process in Nepal?
The FDI process in nepal involves online application through imis.doind.gov.np, obtaining approval from FITT Unit, company incorporation, NRB approval for capital inflow, tax registration, industry registration, bank account opening, and investment remittance through banking channels.
What are the requirements to register Foreign Company?
Requirements include FDI approval, minimum investment of NPR 20 million (except IT companies), project proposal, financial credibility certificate, notarized identification documents, joint venture agreement if applicable, and sector-specific approvals.
How to establish Foreign Company in Nepal easily?
Establishing an IT company is easiest as there’s no minimum investment requirement. The process involves online FDI application, document submission, company registration through OSSC, and completing post-registration formalities with streamlined procedures.
How to obtain FDI Approval in Nepal?
FDI approval requires submitting an online application through imis.doind.gov.np with required documents, including project proposal, financial credibility certificate, and identification documents, followed by processing by the FITT Unit at OSSC.
Can Foreigners obtain Business Visa?
Yes, foreigners can obtain business visas with investment in Nepal. The process requires recommendation from the Department of Industry, proof of investment, and application to the Department of Immigration.
What are the annual compliance of FDI Company?
Annual compliances include filing audited financial statements, annual returns with the Company Registrar, tax filings, industry registration renewal, foreign investment verification with DOI, and sector-specific regulatory requirements.
How can Foreigners Establish Business in Nepal?
Foreigners can establish business by obtaining FDI approval, incorporating a company, bringing in capital through banking channels, completing tax registration, obtaining necessary permits, and fulfilling investment commitments according to the approved timeline.
What are the documents required for obtaining FDI approval in Nepal?
Required documents include the investor’s passport, company registration certificate, board resolution, financial statements, project proposal, tax details, and a commitment letter. Additional sector-specific documents may be necessary for approval.
What is the permissibility requirement for FDI in Nepal?
Foreign investment is allowed in most sectors except those restricted under FITTA 2019. Investors must meet minimum capital requirements, comply with sectoral limitations, and obtain approvals from DOI, IBN, and NRB for investment execution.
What is the minimum capital requirement for FDI approval in Nepal?
As per FITTA 2019, the minimum foreign investment threshold is NPR 20 million (~USD 150,000). However, IT Companies don’t have any minimum thresholds.
What is the timeline for obtaining FDI Approval?
The foreign investment approval process typically takes 30–45 days, depending on the complexity. Delays may occur due to regulatory reviews, additional document requirements, or sector-specific compliance conditions.
Can a foreign investor invest 100% ownership in Nepal?
Yes, foreign investors can hold 100% ownership in most sectors, except for industries restricted under the Negative List of FITTA 2019, which includes defense, retail, real estate, and specific small-scale industries.
What is the current situation of FDI in Nepal?
Nepal’s FDI climate is improving with policy reforms, tax incentives, and infrastructure development. However, bureaucratic hurdles, policy inconsistencies, and regulatory challenges still impact investor confidence and business sustainability.
Who approves FDI in Nepal?
The Department of Industry (DOI) approves general FDI, while the Investment Board Nepal (IBN) handles large-scale projects exceeding NPR 6 billion (~USD 45 million). Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB) regulates foreign currency transactions.
What is the automatic route of FDI in Nepal?
As of October 2, 2023, the Government of Nepal has implemented a streamlined process for approving foreign investments up to NPR 500 million (approximately USD 3.7 million) through an automatic route.
What are the 4 methods of FDI?
Methods of FDI in Nepal
1. Equity Investment (share acquisition in a company).
2. Reinvestment of earnings.
3. Lease financing by foreign investors.
4. Technology transfer agreements tied with capital investment or equity participation.
What is the Foreign Investment Policy in Nepal?
Nepal’s Foreign Investment Policy permits FDI in most sectors with minimum investment of NPR 20 million. Approval is required, and foreign ownership is restricted in negative list sectors. Repatriation is allowed subject to compliance.


